MicroCoat® advances traditional fluid-bed coating with cutting-edge process engineering that minimizes surface adhesion and eliminates particle agglomeration. This innovation shortens coating process times, increases production yield, and enables cost-effective coating of small particles (<250 μm).
MicroCoat® allows coatings for taste masking, once-daily dosing (controlled release), and targeted delivery to the gastrointestinal tract.
The coated micro-pellets can be formulated into oral suspensions, chewable and dispersible tablets, orally disintegrating tablets, or oral films – adapting to various users’ needs.
With its adaptable design, MicroCoat® supports applications across paediatrics, dysphagia care, and veterinary medicine. Its versatility enables user-focused products that are easier to take – improving treatment compliance and user comfort across human and animal health.
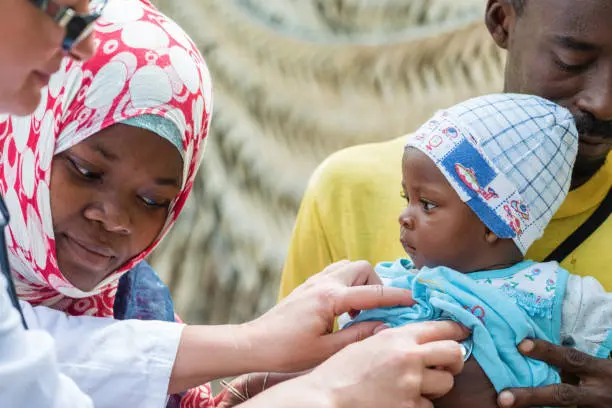
Taste plays a crucial role in the success of paediatric oral formulations. While flavouring agents and sweeteners can mask mild bitterness, they are often ineffective for highly bitter or water-soluble active ingredients.
Our MicroCoat® technology provides an advanced solution by applying a taste-masking membrane that creates a barrier between the drug and taste buds, effectively blocking unpleasant tastes and improving the overall medicine-taking experience for children.
MicroCoat® has been successfully applied to a Unitaid-supported artesunate/amodiaquine therapy for malaria, recognised by the World Health Organisation (WHO) as a Paediatric Drug Optimisation (PADO) priority.

Dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, affects a large proportion of older patients, as well as individuals with neurological, developmental, or medical conditions. Conventional tablets and capsules can be challenging—or even unsafe—for these users to take, often leading to poor adherence and reduced therapeutic outcomes.
Fluid Pharma’s MicroCoat® technology enables the development of easy-to-swallow medicines designed specifically for patients with swallowing difficulties.
By combining formulation innovation with patient-centric design, MicroCoat® helps make treatment simpler for those living with dysphagia.

Administering medicines to companion animals such as cats and dogs can be a major challenge. Many pets resist oral treatments, leading to stress for both animals and owners and reducing compliance. Studies report average adherence rates around 50%, with cats being notoriously more difficult to medicate due to their selective nature.
Fluid Pharma’s MicroCoat® technology offers a practical solution. It produces odourless, and tasteless micro-pellets that can be formulated into liquid suspensions or mixed into pet food.
By eliminating unpleasant taste and smell, MicroCoat® helps ensure stress-free, safe, and reliable administration—improving compliance and protecting the pet-owner bond.
Patel K, Liu, F. Advanced Oral Sustained-Release Drug Delivery Systems for Older Patients. In book: Pharmaceutical Formulations for Older Patients, AAPS Advances in the Pharmaceutical Sciences Series 2023, 51, pp. 129–155
Jani YH, Liu F, Orlu M, Desai N, Du Chayla F, Ruiz F, Vallet T, Medicine acceptability for older people in hospital and care home: the influence of setting, International Journal of Pharmacy Practice, 2022, 30: 67-74
Patel S, Scott N, Patel K, Mohylyuk V, McAuley WJ, Liu F. Easy to Swallow “Instant” Jelly Formulations for Sustained Release Gliclazide Delivery. Journal of Pharmaceutical Science, 2020; 109 (8): 2474-2484.
Scott N, Patel K, Sithole T, Xenofontos K, Mohylyuk V, Liu F. Regulating the pH of bicarbonate solutions without purging gases: Application to dissolution testing of enteric coated tablets, pellets and microparticles. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2020; 30;585:119562.
Mohylyuk V, Patel K, Scott S, Richardson C, Murnane D, Liu F. Wurster fluidised bed coating of microparticles: Towards scalable production of oral sustained-release liquid medicines for patients with swallowing difficulties, AAPS PharSciTech, 2019; 11;21(1):3.
Ranmal SR, O’Brien F, Lopez F, Ruiz F, Orlu M, Tuleu C, Walsh J, Liu F. Methodologies for Assessing the Acceptability of Oral Formulations among children and older adults: A Systematic Review (Keynote Review), Drug Discovery Today. 2018, 23(4):830-847
Ternik R, Liu F, Bartlett JA, Khong YM, Thiam Tan DC, Dixit T, Wang S, Galella EA, Gao Z, Klein S. Assessment of swallowability and palatability of oral dosage forms in children: Report from an M-CERSI pediatric formulation workshop. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2017, 536(2):570-581.
Walsh J, Ranmal SR, Ernest TB, Liu F. Patient acceptability, safety and access: A balancing act for selecting age-appropriate oral dosage forms for paediatric and geriatric populations. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2017, 536(2):547-562.
Merchant HA, Liu F, Orlu Gul M, Basit AW. Age-mediated changes in the gastrointestinal tract. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2016, 512: 382-395.
Liu F, Ghaffur A, Bains J, Hamdy S. Acceptability of oral solid medicines in older adults with and without dysphagia: A nested pilot validation questionnaire based observational study. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2016, 512: 374-381.
Liu F, Ranmal S, Batchelor HK, Orlu-Gul M, Ernest TB, Thomas IW, Flanagan T, Kendall R, Tuleu C, Formulation factors affecting acceptability of oral medicines in children. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2015, 492:341-3.
Liu F, Ranmal S, Batchelor HK, Orlu-Gul M, Ernest TB, Thomas IW, Flanagan T, Tuleu C., Patient-centred pharmaceutical design to improve acceptability of medicines: similarities and differences in paediatric and geriatric populations. Drugs. 2014, 74(16):1871-89.